Similar to the Range Object, the Worksheet has its own set of properties and methods. When we write Excel VBA 365 code involving the Worksheet object, we use Worksheets.
Some of the common properties of the worksheet are name, count, cells, columns, rows and columnWidth.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
MsgBox Worksheets(1).Name
End Sub
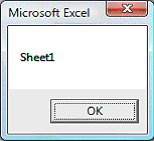
Running the code will produce a pop-up dialog that displays the worksheet name as sheet 1, as shown in Figure 19.1.
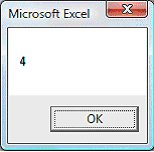
The count method returns the number of worksheets in an opened workbook.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
MsgBox Worksheets.Count
End Sub
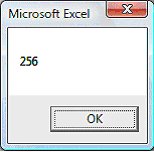
The count method in this example will return the number of columns in the worksheet.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
MsgBox Worksheets(1).Columns.Count
End Sub
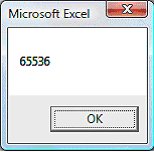
The count method in this example will return the number of rows in the worksheet.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
MsgBox Worksheets(1).Rows.Count
End Sub
Some of the worksheet methods are add, delete, select, SaveAs, copy, paste and more.
In this example, when the user clicks the first command button, it will add a new sheet to the workbook. When the user clicks the second command button, it will delete the new worksheet that has been added earlier.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Worksheets.Add
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click()
Worksheets(1).Delete
End Sub
The select method associated with worksheet lets the user select a particular worksheet. In this example, worksheet 2 will be selected.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
'Worksheet 2 will be selected
Worksheets(2).Select
End Sub
The select method can also be used together with the Worksheet's properties Cells, Columns, and Rows as shown in the following examples.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
'Cell A1 will be selected
Worksheets(1).Cells(1).Select
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
'Column 1 will be selected
Worksheets(1).Columns(1).Select
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
'Row 1 will be selected
Worksheets(1).Rows(1).Select
End Sub
Excel VBA 365 also allows us to write code for copy and paste. Let's look at the following Example:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
'To copy the content of a cell 1
Worksheets(1).Cells(1).Select
Selection.Copy
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click()
'To paste the content of cell 1 to cell 2
Worksheets(1).Cells(2).Select
ActiveSheet.Paste
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton3_Click()
'Protect worksheet with password
Worksheets("Sheet1").Protect Password:="mypassword", _
AllowFormattingCells:=True
End Sub
Private Sub CommandButton4_Click()
'Unprotect worksheet
Worksheets("Sheet1").Unprotect Password:="mypassword"
End Sub
This example shows how to secure your worksheet with password protection while allowing cell formatting.
Worksheets("Data")) rather than index number when possibleWorksheet.Activate before making changes to ensure you're working with the correct sheetVisible property) for better user experienceUsedRange property to work with only the cells that contain dataApplication.ScreenUpdating = False) when making multiple worksheet changes
Found this helpful? Share with other Excel users:
Copyright ® 2023 Dr. Liew Voon Kiong . All rights reserved [Privacy Policy]
Contact: Facebook Page