The Select Case control structure also involves decisions making but it is slightly different from the If...Then...ElseIf control structure . The If ...Then...ElseIf statement control structure evaluates only one expression but each ElseIf statement computes different values for the expression. On the other hand, the Select Case control structure evaluates one expression for multiple values. Select Case is preferred when there exist multiple conditions as using If...Then...ElseIf statements will become too messy.
The syntax is as follow
Select Case variable Case value 1 Statement Case value 2 Statement Case value 3 Statement Case value 4 Statement Case Else End Select
In the following example, we shall show you how to process the grades of students according to the marks given.
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click()
Dim mark As Single
Dim grade As String
mark = Cells(1, 1).Value
Range("A1:B1").Select
With Selection
.HorizontalAlignment = xlCenter
End With
Select Case mark
Case 0 To 20
grade = "F"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case 20 To 29
grade = "E"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case 30 To 39
grade = "D"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case 40 To 59
grade = "C"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case 60 To 79
grade = "B"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case 80 To 100
grade = "A"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
Case Else
grade = "Error!"
Cells(1, 2) = grade
End Select
End Sub
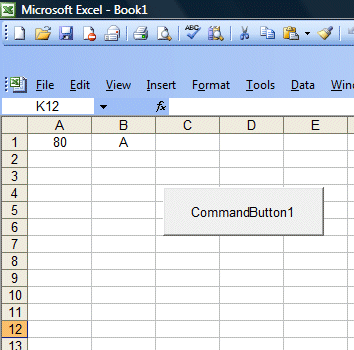
You should also include the error case where the values entered are out of the range or invalid. For example, if the examination mark is from 0 to 100, then any value out of this range is invalid. In this program, we use case else to handle the error entries.The Figure below shows the output of this example.
Copyright ® 2008 Dr.Liew Voon Kiong . All rights reserved [Privacy Policy]
Contact: Facebook Page