[Lesson 21]<<[Table of Contents]>>[Lesson 23]
22.1 The CheckBox
The Checkbox and option button allows the user to select one or more items by checking the check box or check boxes concerned. For example, you may create a shopping cart where the user can click on checkboxes that correspond to the items they intend to buy can calculate the total payment.
One of the most important properties of the checkbox in Excel 2010 VBA is Value. If the checkbox is selected or checked, the value is true, whilst if it is not selected or unchecked, the Value is False.
Example 22.1
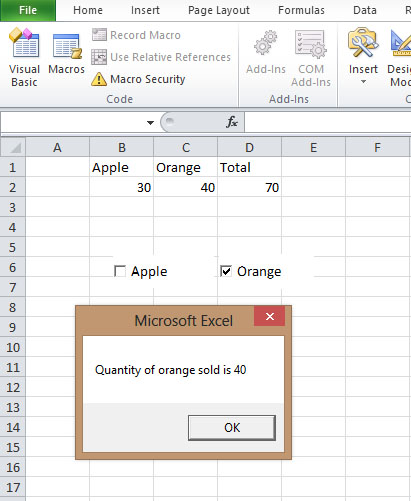
In this example, the user can choose to display the sale volume of one type of fruits sold or total sale volume. The code is shown below:
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() If CheckBox1.Value = True And CheckBox2.Value = False Then MsgBox “Quantity of apple sold is” & Cells (2, 2).Value ElseIf CheckBox2.Value = True And CheckBox1.Value = False Then MsgBox “Quantity of orange sold is ” & Cells(2, 3).Value Else MsgBox “Quantity of Fruits sold is” & Cells (2, 4).Value End If End Sub
The output Interface is shown in Figure 22.1
Figure 22.1
22.2 Option Button
The option button control also lets the user selects one of the choices. However, two or more option buttons must work together because as one of the option buttons is selected, the other option button will be deselected. In fact, only one option button can be selected at one time. When an option button is selected, its value is set to “True” and when it is deselected; its value is set to “False”.
Example 22.2
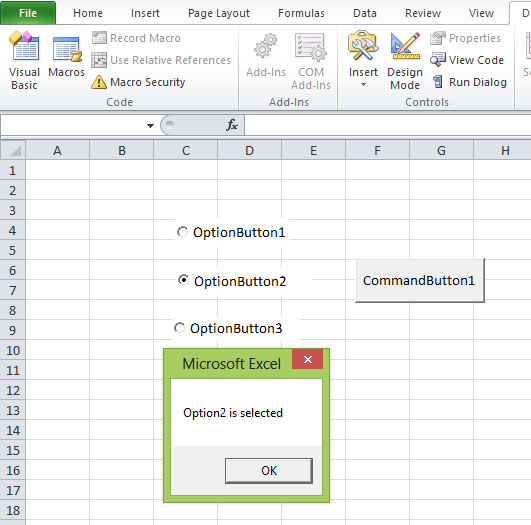
This example demonstrates the usage of the option buttons. In this example, the Message box will display which option button selected by the user. The output interface is shown in Figure 22.2.
The code
Private Sub CommandButton1_Click() If OptionButton1.Value = True Then MsgBox "Option1 is selected" ElseIf OptionButton2.Value = True Then MsgBox "Option2 is selected" Else MsgBox "Option3 is selected" End If End Sub
The output